概念
可视化网站 https://visualgo.net/zh
时间频度
一个算法中的语句执行次数称为语句频度或时间频度,T(n)
如:计算1-100所有数字之和:
- for循环,从1加到100,T(n)=n+1计算n次,判断一次
- 利用等差数列数学公式(首项+末项)*项数/2,T(n)=1
时间复杂度 Time Complexity
- 事后统计,统计运行程序的时间,绝对值,耗时,与计算机硬件相关
- 事前估算,分析某个算法的时间复杂度
若存在一个辅助函数f(n),当n趋近于正无穷时,f(n)/T(n)=C 即等价无穷大,记作:T(n)=O(f(n)),称其为算法的渐进时间复杂度,简称时间复杂度。计算方法:如3n^2+2n+10
- 用常数1代替时间频度中的所有加法常数 n^2+n+1
- 只保留最高次项 n^2
- 去除最高阶项的系数 n^2
常见时间复杂度
由小到大排序:
- O(1) 常数阶
- O(log2n) 对数阶
- O(n) 线性阶
- O(nlog2n) 线性对数阶
- O(n^2) 平方阶 (双重for循环)
- O(n^3) 立方阶 (三重for循环)
- O(n^k) k次方阶 (k重for循环)
- O(2^n) 指数阶 (尽量避免出现)
平均、最坏时间复杂度
所有可能输入均以等概率出现时算法运行的时间为平均时间复杂度,最坏时间复杂度,算法运行时间不会比最坏情况下更长
平均时间复杂度和最坏时间复杂度是否相同和算法相关。
空间复杂度 Space Complexity
算法运行过程中所耗费的存储空间的大小,一般更看重时间复杂度。如某些 Copy To RAM 程序
排序算法 Sort Algorithm
可视化参考https://visualgo.net/zh/sorting
排序分为内部排序和外部排序。
- 内部排序指把数据全部加载近内存中进行排序
- 外部排序需要借助外存来排序(数据量很大时)
冒泡排序 Bubble Sorting
重复循环:从左到右依次比较相邻元素大小,如果arr[i]>arr[i+1],则交换位置
因为排序各元素不断接近自己的位置,如果一趟比较下来没有进行交换,就说明序列有序,因此在排序过程中设置一个 flag 判断是否进行过交换,减少不必要的比较。
public class Bubble {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] Array = {29, 10, 14, 37, 14};
BubbleSort bubbleSort = new BubbleSort(Array);
bubbleSort.sort();
bubbleSort.print();
}
}
class BubbleSort {
private int[] array;
BubbleSort(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
/* original
public void sort() {
boolean flag=false;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
swap(j);
}
}
}
}
*/
public void sort() {
boolean swapflag = true;
while (swapflag) {
swapflag = false;
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - count; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
swap(j);
swapflag = true;
count++;
}
}
}
}
/**
* swap arr[index],arr[index+1]
* @param j index of arr
*/
private void swap(int j) {
int temp;
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
public void print() {
for (int j : array) {
System.out.print(j + ",");
}
}
}关于时间统计,写一单独的测试类如下,测试十万个数据,在 Linux 下使用 time 命令, Windows 下使用 Measure-Command 下略。
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size=100000;
int[] array = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i]=(int)(Math.random()*size);//get number in [0,size)
}
BubbleSort bubbleSort = new BubbleSort(array);
bubbleSort.sort();
System.out.println("finished");
}
}选择排序 Select Sorting
假定当前数为最小,不断查找最小数据,遍历到最后时,得到最小数,将最小数与数组未排序部分的最前端交换位置
- 进行数组大小size-1次排序
- 每轮排序是一个循环
public class Select {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] Array = {29, 10, 14, 37, 14};
SelectSort selectSort = new SelectSort(Array);
selectSort.sort();
selectSort.print();
}
}
class SelectSort {
private int[] array;
SelectSort(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public void sort() {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
int min = array[i];
for (int j = i; j < array.length; j++) {
if (min > array[j]) {
min = array[j];
minIndex = j;
}
}
swap(i, minIndex);
}
}
/**
* swap arr[index1],arr[index2]
*
* @param i index1
* @param j index2
*/
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int temp;
temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
public void print() {
for (int j : array) {
System.out.print(j + ",");
}
}
}使用命令统计时间后,可以发现:对于随机数据选择排序相对于冒泡排序来说快了一些。
插入排序 Insert Sorting
- 将数组分为有序区和无序区(初始有序区只有第一个元素)
- 每次从无序区拿取一个元素,插入有序区中合适的位置(比它大的index+1,直至找到比它小的)
对应条件
- 初始有序区有一个元素,固从i=1开始取
- 定义一个临时变量,拿取无序区的第一个元素
- 将这个变量和有序区的最后一个元素 array[j](j=i-1) 比较
- 临时变量小于array[j],最后一个元素向右移动,array[j+1]=array[j],并继续向前判断 j–,直至j<0
- 否则直接插入当前位置array[j+1]=temp
public class Insert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] Array = {29, 10, 14, 37, 14};
InsertSort insertSort = new InsertSort(Array);
insertSort.sort();
insertSort.print();
}
}
class InsertSort {
private int[] array;
InsertSort(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public void sort() {
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
int j;
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && array[j] > temp; j--) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
}
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
public void print() {
for (int j : array) {
System.out.print(j + ",");
}
}
}
可以发现即使三种算法的时间复杂度相同,但是实际运算时间却不同,主要由元素交换的次数造成。时间:
冒泡>选择>插入
插入排序存在的问题
虽然插入排序是上面的排序方法中速度最快的,但仍有一些问题:
- 排序数组 {2,3,4,5,6,1}时后移次数明显增多
- 对于大规模乱序数组插入排序效率不够高,因为它只会交换相邻的元素,因此元素只能一点一点地从数组的一端移动到另一端
希尔排序 Shell Sorting
希尔排序对插入排序进行优化,也称缩小增量排序。希尔排序的思想是使数组中任意间隔为 h 的元素都是有序的。然后将 h 减小,当 h 为 1 时,这就是一次普通的插入排序。
这样的数组被称为 h 有序数组。如果 h 很大,我们就能将元素移动到很远的地方,为实现更小的 h 有序创造方便。
那么 h 是一个什么样的序列(数列)对排序的性能有一定影响,Shell 最初建议步长选择为 n/2,并且对步长取半直到步长达到1,但仍有更优的序列。对于不同的序列可参考 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shellsort
public class Shell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] Array = {29, 10, 14, 37, 14};
shellSort shellSort = new shellSort(Array);
shellSort.sort();
shellSort.print();
}
}
class shellSort {
private int[] array;
shellSort(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public void sort() {
int temp;
for (int step = array.length / 2; step > 0; step /= 2) {
for (int i = step; i < array.length; i++) {
temp = array[i];
int j;
/*
* j >= step make array[j - step] work
* array[j] and array [i] are same group
* j -= step go back to check
* */
for (j = i; j >= step && array[j - step] > temp; j -= step) {
array[i] = array[j - step];
}
array[j] = temp;
}
}
}
public void print() {
for (int j : array) {
System.out.print(j + ",");
}
}
}快速排序 Quick Sorting
快速排序时对冒泡排序的改进,通过一次排序,将要排序的数据分割成两部分,其中一部分的所有数据比另一部分的所有数据都小(随机取一个基准,比该基准小的放在左边,比它大的放在右边),再将每一部分其一分为2,再次排序,以此往复。
- 随机挑选一个基准值,以数组中间的值(pivot)为例,中间值就把数组分成了两半
- 左边一组,从左到右,挨个与 pivot 比较,找出一个比 pivot 大的值
- 右边一组,从右到左,挨个与 pivot 比较,找出一个比 pivot 小的值
- 左右两边各找到一个值,那么就让这两个值进行交换
- 然后继续找,直到左右两边碰到,这一轮就结束
- 继续对分出来的组,进行上述操作,直到每组内只剩下一个数
public class Quick {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {29, 10, 14, 37, 14};
QuickSort quickSort = new QuickSort(array);
quickSort.sort(0, array.length - 1);
quickSort.print();
}
}
class QuickSort {
private int[] array;
QuickSort(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public void sort(int left, int right) {
int l = left;
int r = right;
// pivot can use array[random number]
int pivot = array[right + (left - right) / 2];
while (l < r) {
// find from left to right until find a number larger than the pivot
while (array[l] < pivot) {
l++;
}
// find from right to left until find a number smaller than the pivot
while (array[r] > pivot) {
r--;
}
// didn't find than break
// all numbers in left smaller than the pivot
// all numbers in right larger than the pivot
if (l >= r) {
break;
}
swap(l, r);
//the next round, the value on the left and right will no longer participate in sorting
//they have been exchanged, it must be smaller than the benchmark value
r--;
l++;
}
// After finding it in a round, if it is not found
// they will no longer participate
if (l == r) {
l++;
r--;
}
if (left < r) {
sort(left, r);
}
if (right > l) {
sort(l, right);
}
}
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int temp;
temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
public void print() {
for (int j : array) {
System.out.print(j + ",");
}
}
}
归并排序 Merge Sorting
采用分治策略,把一个大问题分解为小问题,然后递归求解。将一个待排序的数组不断分成两份,进行排序,O(n)=n-1 有非常低的时间复杂度
public class Merge {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {29, 10, 14, 37, 14};
MergeSort mergeSort = new MergeSort(array);
mergeSort.sort(0, array.length - 1);
mergeSort.print();
}
}
class MergeSort {
private int[] array;
private int[] temp;
MergeSort(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
this.temp = new int[array.length];
}
public void sort(int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) return;
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
sort(left, mid);
sort(mid + 1, right);
merge(left, right, mid);
}
}
/**
* merge method
*
* @param left first index of left array
* @param right first index of right array
* @param mid middle index
*/
public void merge(int left, int right, int mid) {
int i = left; //init i, first index of left array
int j = mid + 1; //init j, first index of right array
int k = 0; //index of temp
// fill temp array with left array and right array
// until one of left and right do not have element.
while (i <= mid && j <= right) {
// if one of left array's element <= right array's element
// fill temp with left array's element
// else fill temp with right array's element
if (array[i] < array[j]) {
temp[k] = array[i];
i++;
} else {
temp[k] = array[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// fill temp with the other array
while (i <= mid) { //left array remain elements
temp[k] = array[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while (j <= right) { //right array remain elements
temp[k] = array[j];
j++;
k++;
}
// copy temp to array
k = 0;
int tempLeft = left;
while (tempLeft <= right) {
array[tempLeft] = temp[k];
k++;
tempLeft++;
}
}
public void print() {
for (int j : array) {
System.out.print(j + ",");
}
}
}上述是使用递归写的归并排序,通过分析可以发现先把数组前两个元素拿出来比较,然后逐渐增加,也可用迭代(循环嵌套)来写。
基数排序 Radix Sorting
- 用10个桶(队列,利用二维数组)代号0到9来存储数据
- 依次将数据的个位数和队列的代号匹配后入队列
- 按照队列的代号顺序依次将元素出队列放回原数组
- 再按照上面的方式比较十位数、百位数直至完毕
提取指定位数的方法
- 12345/1%10=5
- 12345/10%10=4
- 12345/100%10=3
- 12345/1000%10=2
- 12345/10000%10=1
基数排序需要使用11个(10个桶换位1个数组)相同大小的数组,需要占用大量的内存,基数排序是效率最高的稳定的排序算法
public class Radix {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {29, 10, 14, 37, 14};
RadixSort radixSort = new RadixSort(array);
radixSort.sort();
radixSort.print();
}
}
class RadixSort {
private int[] array;
RadixSort(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public void sort() {
//get max number
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] > max) {
max = array[i];
}
}
//get digits of max number
int maxLength = (max + "").length();
int n = 1; // helper: get a digit of element
int[][] bucket = new int[10][array.length]; // ten buckets
int[] bucketElementCount = new int[10]; // record how many element in each bucket
for (int i = 0; i < maxLength; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
int digitOfElement = array[j] / n % 10;
bucket[digitOfElement][bucketElementCount[digitOfElement]] = array[j];
bucketElementCount[digitOfElement]++;
}
//copy to original array
int index = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) {
if (bucketElementCount[k] != 0) {
for (int l = 0; l < bucketElementCount[k]; l++) {
array[index] = bucket[k][l];
index++;
}
}
bucketElementCount[k] = 0;
}
n *= 10;
}
}
public void print() {
for (int j : array) {
System.out.print(j + ",");
}
}
}查找算法 Search Algorithm
常用的查找算法:
- 顺序(线性)查找
- 二分/折半查找
- 插值查找
- 斐波那契查找
线性查找 Linear Search
名字好听,就是个暴力查找,遍历一遍,相等就输出,唯一好处就是不用给数组排序,略了。
二分查找 Binary Search
可参考 二分查找详解
需要先将数据排好队,然后才能查找。算法简单,例如猜数字游戏:
- 随机给出一个0-100之间的数字(如76)
- 猜50(0+(100-0)/2),得到回应:小了
- 猜75(50+(100-50)/2),得到回应:小了
- 猜87(75+(100-75)/2),得到回应:大了
- 猜81(87-(87-75)/2),得到回应:大了
- 猜78(81-(81-75)/2),得到回应:大了
- 猜77(78-(78-75)/2),得到回应:大了
- 猜76,结束
使用上述方法,至多7步就可以得到结果
总结一下左边界为 left ,右边界为 right ,中间值为 mid ,mid=left+(right-left)/2
代码中 left + (right – left) / 2 就和 (left + right) / 2 的结果相同,但是有效防止了 left 和 right 太大直接相加导致溢出。
二分查找的易错问题:左右区间,如何再开、闭、半开半闭、半闭半开区间内查找,mid值是否应该+1
基本的二分查找
搜索一个数,如果存在,返回其索引,否则返回 -1。
# left 和 righ 的初始值 与 while 循环的条件
while 循环的条件是 <=,而不是 <
初始化 right 的赋值是 array.length – 1,即最后一个元素的索引,而不是 array.length。
这二者可能出现在不同功能的二分查找中,区别是:前者相当于两端都闭区间 [left, right],后者相当于左闭右开区间 [left, right),因为 array[array.length] 是越界的。
while(left <= right) 的终止条件是 left == right + 1,写成区间的形式就是 [right + 1, right],这时区间为空
while(left < right) 的终止条件是 left == right,写成区间的形式就是 [right, right],这时区间里的数为 right,这个数还没有被判断
# left = mid + 1 与 right = mid – 1
因为搜索区间是 [left, right] ,为闭区间,那么当发现索引 mid 不是要找的 target 时,应搜索 [left, mid-1] 或者 [mid+1, right],因为mid 已经搜索过了。
public class Binary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Search search = new Search();
System.out.println("index:"+search.search());
}
}
class Search {
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int target=5;
int left = 0;
int right = array.length - 1;
public int search() {
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (array[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (array[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}这个二分查找还不完善,例如数组中有多个相同的值,上述程序无法查找。
插值查找 Interpolation Search
当使用二分查找查找第一个元素时,它需要多次查找,速度还不如线性查找,对 mid 的取值进行优化,得到插值查找。举例:
使用二分查找,查找{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18}数组中 1 的 index。
插值查找将 mid 值改为一个数学公式:
二分:mid=left+(right-left)/2
插值:mid=left+(right-left)*(target-array[left])/(array[right]-array[left])
插值查找的公式推导可参考 Demystifying Interpolation formula for Interpolation Search 数学原理非常简单。
对于一个一次函数 f(index)=k*index+b (将函数自变量 x 换为数组的 index 值)。该公式是直接算出来要查找的值在哪。
因此可以推断出:对于数据量大,且数据分布均匀的数组,使用插值查找非常迅速,但是对于数据分布不均匀的数组,插值查找不一定优于二分查找
代码实现与二分查找相同,只更改mid的计算方式。
斐波那契查找 Fibonacci Search
背景
斐波那契查找也叫黄金分割查找
- 黄金分割是把一条线段分成 a 和 b 两部分,使a/(a+b)=b/a,这个比值近似为0.618
- 斐波那契数列{0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21}后面的值为前两项的和,相邻两数的比值近似为0.618
同插值查找一样,斐波那契查找将 mid 值改为一个数学公式:
二分:mid=left+(right-left)/2
插值:mid=left+(right-left)*(target-array[left])/(array[right]-array[left])
斐波那契:mid=left=F(k-1)-1
F为斐波那契数列,F(k)为斐波那契数列的第k项
同样的,可以理解为:斐波那契查找也将数列分成 a、b 两部分,然后根据 mid 的值与 target 比较,继续将某一段分为两部分,实际上斐波那契查找和二分法查找性能相似。当数组中的数字个数不是斐波那契数列中的数时,需要增加一些项即一次或多次复制数组的最后一项,并添加到数组末尾。
while循环的条件则需换为 while(n>F(k)-1)
实际上斐波那契查找的性能与二分法近似。
哈希表 Hash Table
问题
有一个公司,当有新的员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入 (id,性别,年龄,住址..), 当输入该员工的 id 时,要求查找到该员工的所有信息。要求:不使用数据库、尽量节省内存、速度越快越好。
对上面这个问题可以使用哈希表来解决。
背景
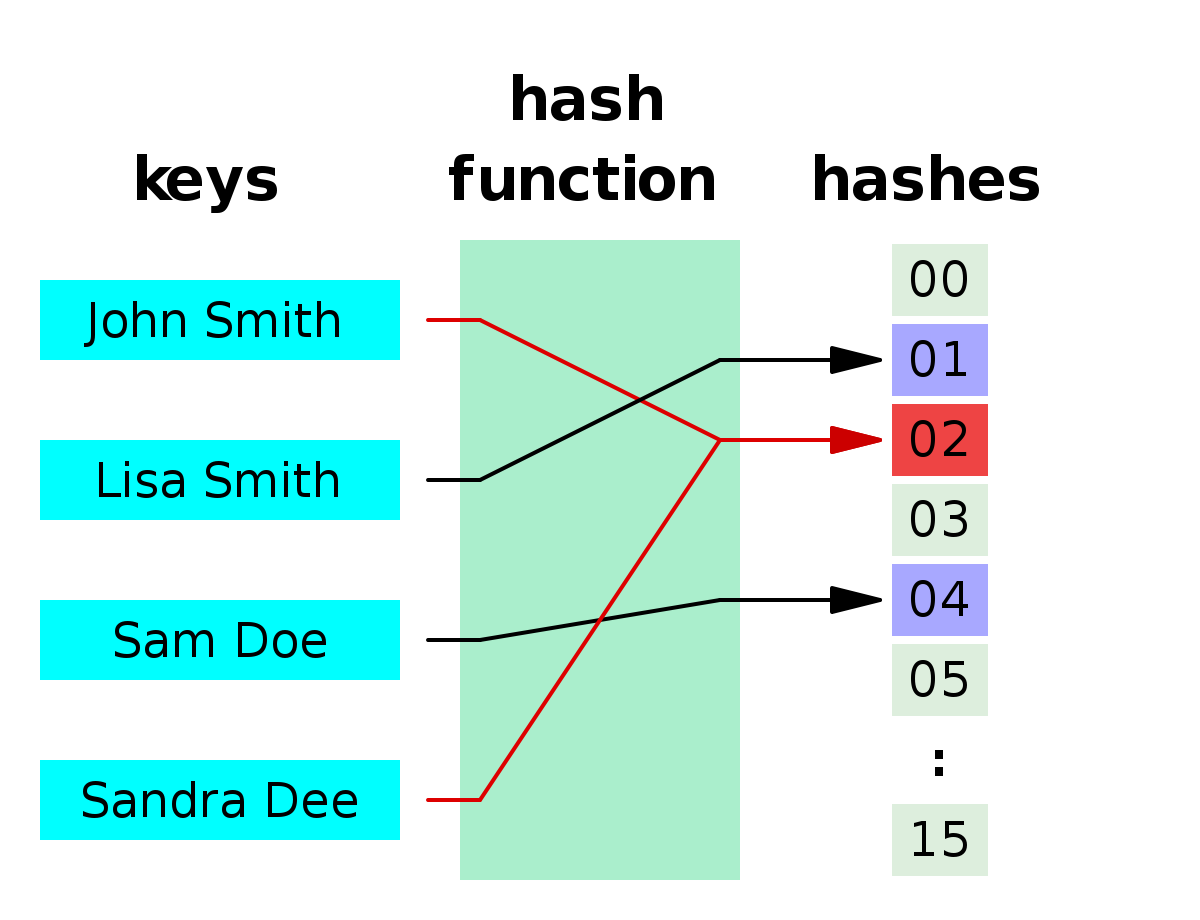
哈希函数(散列函数)就是将一个输入转化成另一种输出,不管输入有多少种不同的类型,输出的长度始终是那么多。那么根据原文件可以直接求出哈希值,但是使用哈希值没有办法求出原文件。
当两个不同的值经过哈希函数处理后,有一定的可能性相等,当不同输入对应同一个值时就发生了散列碰撞,如上图。从数学上来说没有可能杜绝碰撞发生,但实际上,如果将哈希值的长度扩展到足够长,加上一定的算法,可将其概率转化为小概率事件,认为碰撞不可能发生。
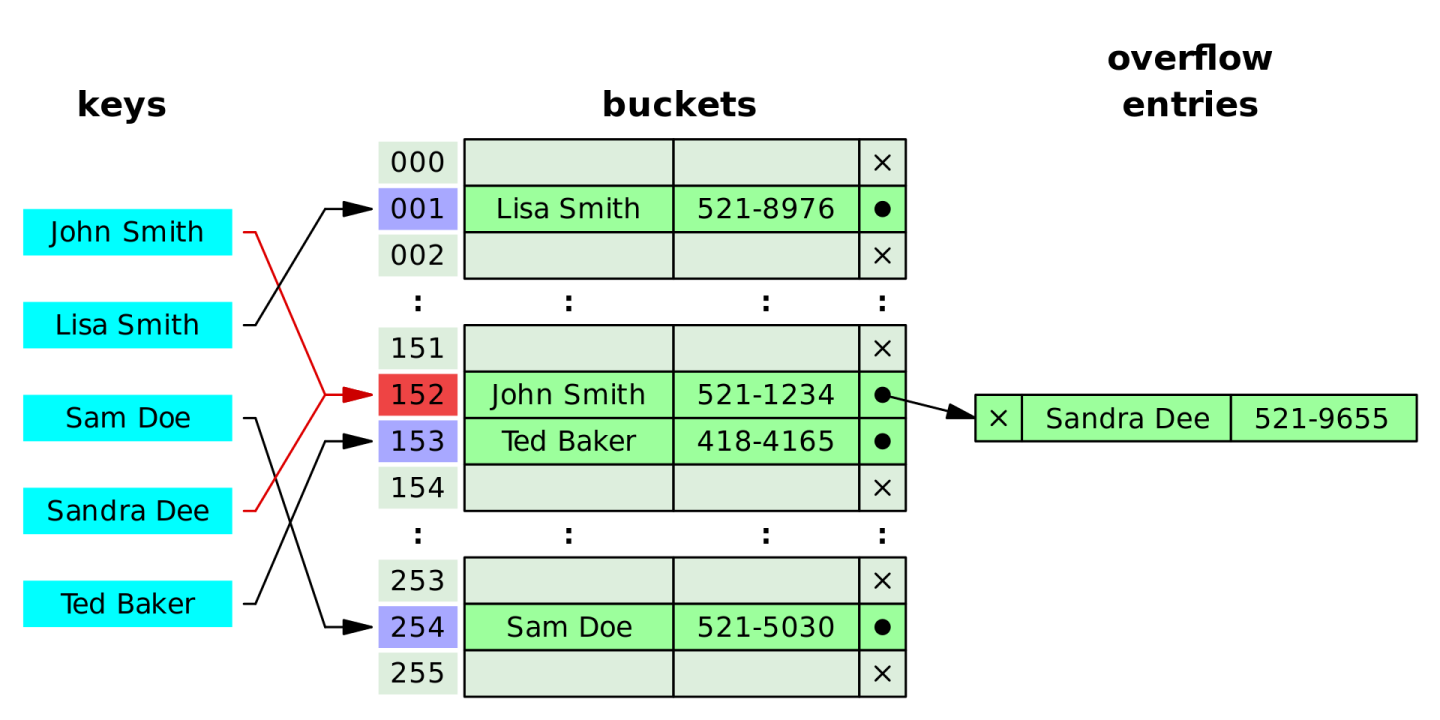
散列表(Hash table),也叫哈希表,是根据 关键码值(key value)直接进行访问的数据结构。
也就是说,它通过关键码值映射到表中的一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表 。
一般常用 数组+链表 或 数组+树 的形式来模拟哈希表。